Finding the remains of a high priest buried at the most sacred spot in Paris’s Notre Dame Cathedral, and all of medieval France, seems a predictable discovery. However, unearthing a knight with an elongated skull came as something of a shock.
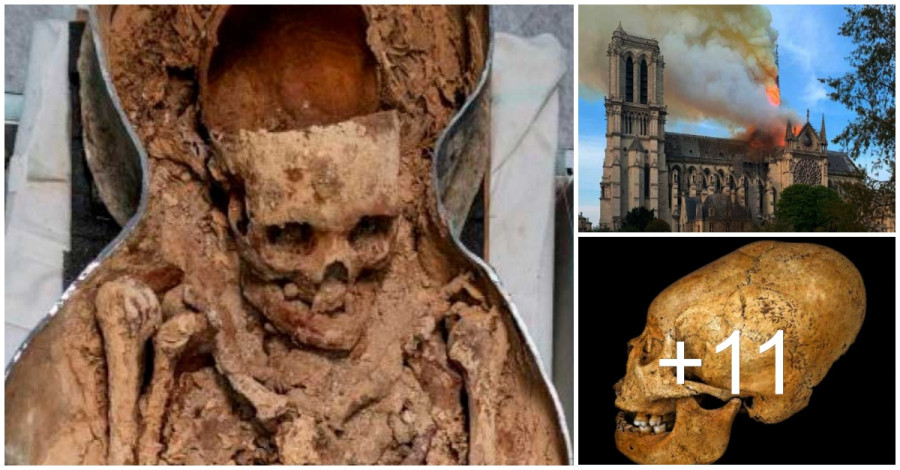

The foundation stone of Notre Dame Cathedral was laid by Pope Alexander III in 1163 AD, but in 2019 a fire almost entirely destroyed it. After having spent the last two years securing its foundations, work began this year on repairing the oak spire that was unveiled on August 18, 1859. This 19th century spire reached a height of 315 feet (96 meters), which was 59 feet (18 meters) higher than the original 12th century spire, but it came crashing down in the aftermath of the 2019 blaze.
It was directly beneath the spire floor, where the transept crosses the nave, that researchers identified several tombs containing hundreds of fragmented hands, feet, faces, and plants from stone statues. It was among these shattered relics that two well-preserved lead sarcophagi were discovered, buried at what represents the holiest site in all of medieval France .

The 2019 fire that engulfed the cathedral indirectly led to the discovery of these Notre Dame sarcophagi (Wandrille de Préville / CC BY SA 4.0 )
Unearthing the Canon and the Knight
In April this year, Professor Christophe Besnier, the leader of the scientific team, told The Guardian that this discovery was both “extraordinary and emotional.” Ancient Origins reported in April that Dominique Garcia, the head of the National Institute of Archaeological Research, speculated that one of the lead sarcophagi “probably belonged to a dignitary from the early 14th century.”
Now, the team of French archaeologists has confirmed that Garcia’s speculations were accurate, as they announce one coffin contains an “elite canon of cathedral ” while the other hosts “a young cavalier (knight).” Dominique Garcia was quick to remind that these human remains “are not archaeological objects,” for they were recovered from within a church, and therefore they “will be treated with respect from beginning to end.”

Opening of the sarcophagi at the Toulouse forensic medicine laboratory. Credit: DR UT3
Buried at the Heart of the Cathedral
The fragmented statues and two lead coffins were discovered beneath the floor of the transept crossing. The transept of a church separates the nave from the chevet (choir), belonging equally to the main nave axis and to the transept. Eric Crubézy, professor of biological anthropology at the University of Toulouse III, said the two men were “clearly important in their respective eras to have been buried in such prestigious tombs at the heart of the cathedral”.

Described as of “remarkable scientific quality,” both burials were found during a speculative subterranean dig before the installation of the 98 foot (30 meter) high, 600-ton scaffold that is being used to replace the cathedral’s fire-damaged spire. A report in The Guardian stated that one of the bodies belonged to a high priest who, after leading a sedentary life, died in 1710 AD. The second lead coffin was dated to the 14th century and contained “a young, wealthy, and privileged noble.”
Who Were these Elites Buried at the Heart of the Cathedral?
Buried one meter deep, the holy man was found with a brass plaque confirming he was Antoine de la Porte, the canon of Notre Dame Cathedral, who died on Christmas Eve 1710 at the age of 83. De la Porte was a clever, influential, and rich old priest who commissioned several works of art that are now in the Louvre. The second coffin was found to contain the remains of a man in his thirties, and the researchers say his pelvic bones suggest he was an experienced horseman. So, he has been named “ Le Cavalier ” (the knight).

The knight was interred at the foot of a large cross that was once displayed on the now-destroyed rood screen that separated the chancel and nave (clergy and choir) from the congregation (poor people with diseases). Cloths and organic plant materials discovered in this burial suggest the knight was embalmed, which the archaeologists say was “a rare practice in the Middle Ages .” Moreover, the knight was buried with a crown of flowers.
It is speculated that this man was of the upper echelons of the 14th century French elite. This belief stems not from his floral crown, nor the fact that he was embalmed, and not even because he had the power to demand burial at the most sacred spot in Paris – but because the dead knight had a “ skull deformation ,” better known as an elongated skull.
Headbanding for Power, All Over the World
The knight had a “deliberately deformed skull,” resulting from having had a tight cloth band tied around his head during his first three months of life, inducing the shape change. In the 1920s, Peruvian archaeologist Julio Tello , the “father of Peruvian archaeology,” uncovered hundreds of elongated Paracas civilization skulls dated to between 750 BC and 100 AD, and they have since been unearthed across the Middle East and Asia.

Elongated skulls, like the one discovered in the Notre Dame sarcophagus, were characteristic of the Paracas Culture (Didier Descouens / CC BY SA 4.0 )
It is generally agreed that cranial banding and the resulting elongated skulls were symbols of power practiced among controlling families in different countries. However, long after the practice died out in Peru, it continued up to the early 20th century in the region of Deux-Sèvres in western France. Here, too, the practice was a symbol of power among social elites, but it was also practiced among poorer families who tried to align their children with higher social classes.
Source: nhadep99.com